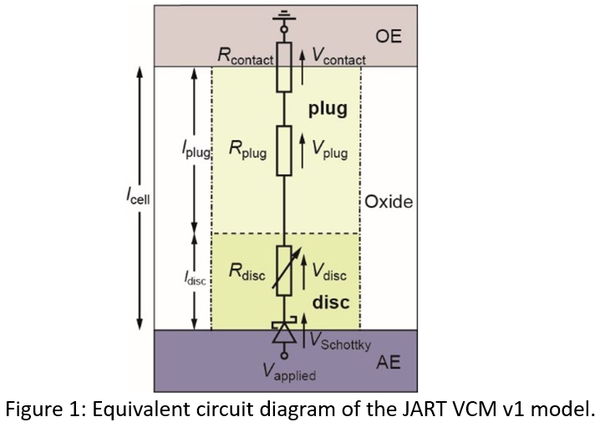
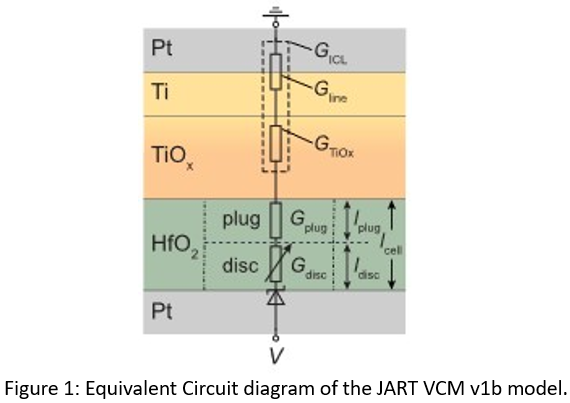
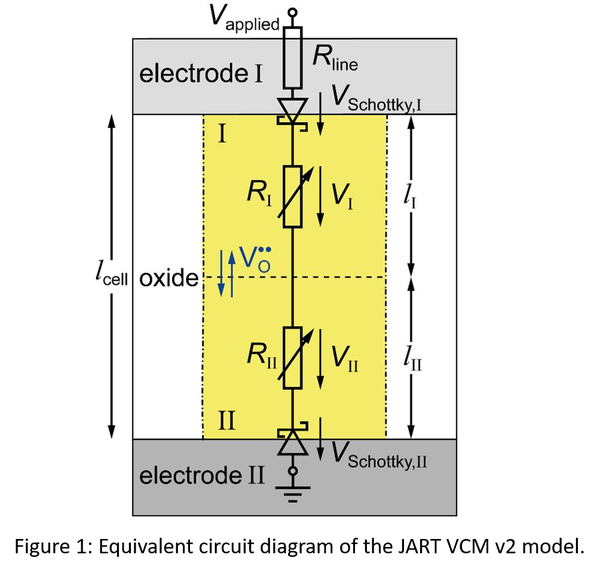
The JART VCM v1 model was developed to simulate the switching characteristics of devices based on the valence change mechanism (also called OxRAM). In this model, the ionic defect concentration (oxygen vacancies) in the disc region close to the active electrode (AE) (see Figure 1) defines the resistance state. The concentration changes due to the non-isothermal drift of the ionic defects. In this model, Joule heating is considered, which significantly accelerates the switching process at high current levels.
The model was developed to study the two-step SET process of VCM cells [1] and the influence of an intrinsic series resistance on the switching characteristics [2].
The Verilog-A code and a stand-alone MATLAB App of this model can be downloaded here. To use the MATLAB app the downloaded file needs to be executed. During the first installation, the MATLAB runtime environment will be downloaded from the internet.
JART VCM v1 STO parameter set
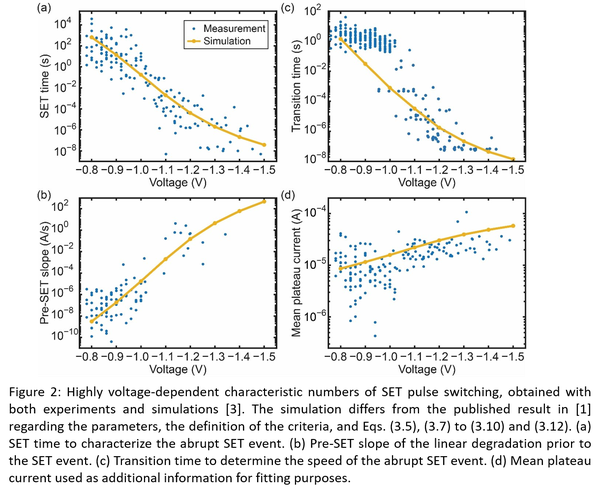
The JART VCM v1 model can be used for different filamentary bipolar resistive switching material systems based on the Valence Change Mechanism. A different parameter set for this model is displayed in Table 1. It has recently been fitted again to the STO cells presented in [1].
The results from Figure 2 can be obtained by exchanging the fitting parameters with the ones in Table 1.
[1] K. Fleck, C. La Torre, N. Aslam, S. Hoffmann-Eifert, U. Böttger and S. Menzel, Uniting Gradual and Abrupt SET Processes in Resistive Switching Oxides, Phys. Rev. Applied 6, 064015 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevApplied.6.064015
[2] A. Hardtdegen, C. La Torre, F. Cüppers, S. Menzel, R. Waser and S. Hoffmann-Eifert, Improved Switching Stability and the Effect of an Internal Series Resistor in HfO2/TiOx Bilayer ReRAM Cells, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 65, 3229-3236 (2018). DOI: 10.1109/TED.2018.2849872
[3] C. La Torre, Physics-Based Compact Modeling of Valence-Change-Based Resistive Switching Devices, Dissertation RWTH Aachen, pp. 48 ff. 2019. http://publications.rwth-aachen.de/record/765751
S. Menzel, C. Bengel