Stretcher Systems
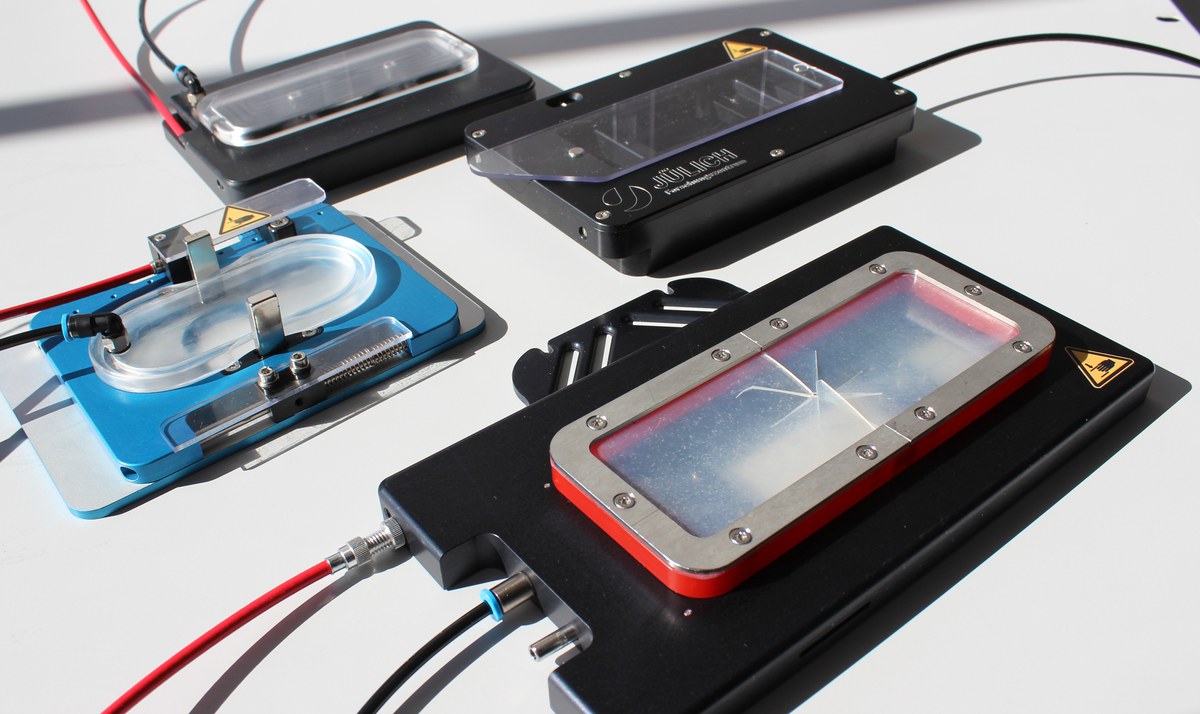

Uniaxial Single Stretcher System
Cells in living organisms are constantly subjected to various mechanical stimuli. One of those is cyclic stretch, which can be found e.g. around blood vessels. Mammalian cells are known to sense such stretch and to reorient their cytoskeleton and shape to maintain homeostasis. Cell-stretchers are used to investigate these processes. We present a fast uniaxial cell stretcher based on a linear stage which is driven by a progammable stepper motor in order to open a wide range of experimental conditions. Stretch parameters can be widely adjusted in terms of e.g. amplitude, frequency and number of cycles. Even at stretch amplitudes of 20% frequencies of up to 5 Hz can be achieved. With this special design, the Uniaxial Stretch System can also be used for live imaging on various microscopes.
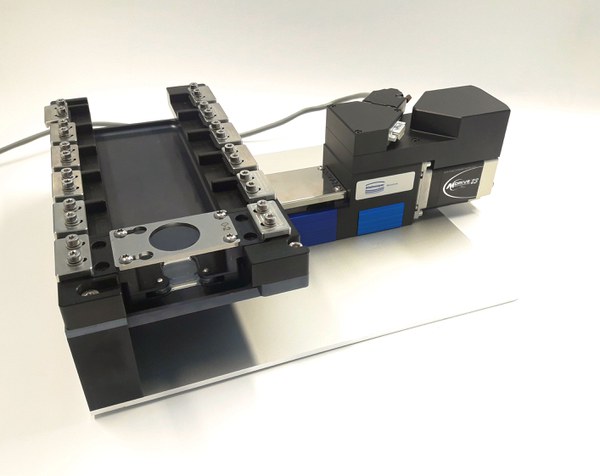
Uniaxial 6x Stretcher System
Modern cell stretch devices simulate mechanical stress in cell culture and typically afford the subsequent analyses in large numbers. The parallel characterization of hundreds of cells within every single experiment enables the identification of even tiny alterations of cellular responses [2]. As seemingly tiny differences in mechanical and cell biological parameters between different measurements often cause surprisingly large variations in cell behaviour, these often limit the statistical significance of experimental results. To minimize those problems all relevant data sets that need to be compared should be handled as parallel as possible. Unfortunately, such parallel handling is hardly feasible for cyclic stretch experiments using expensive experimental setups and experimental duration often in the 24 hours range.
To overcome those problems and to increase experimental validity we developed a new, fast uniaxial cell stretcher based on a commercial linear axis with stepper motor drive and integrated controller for a holding capacity of up to 6 stretch chambers in parallel. The freely programmable computer aided motion control in combination with a fast stepper motor allows for a wide range of experiments from slow cell deformations up to fast heart beat simulations.
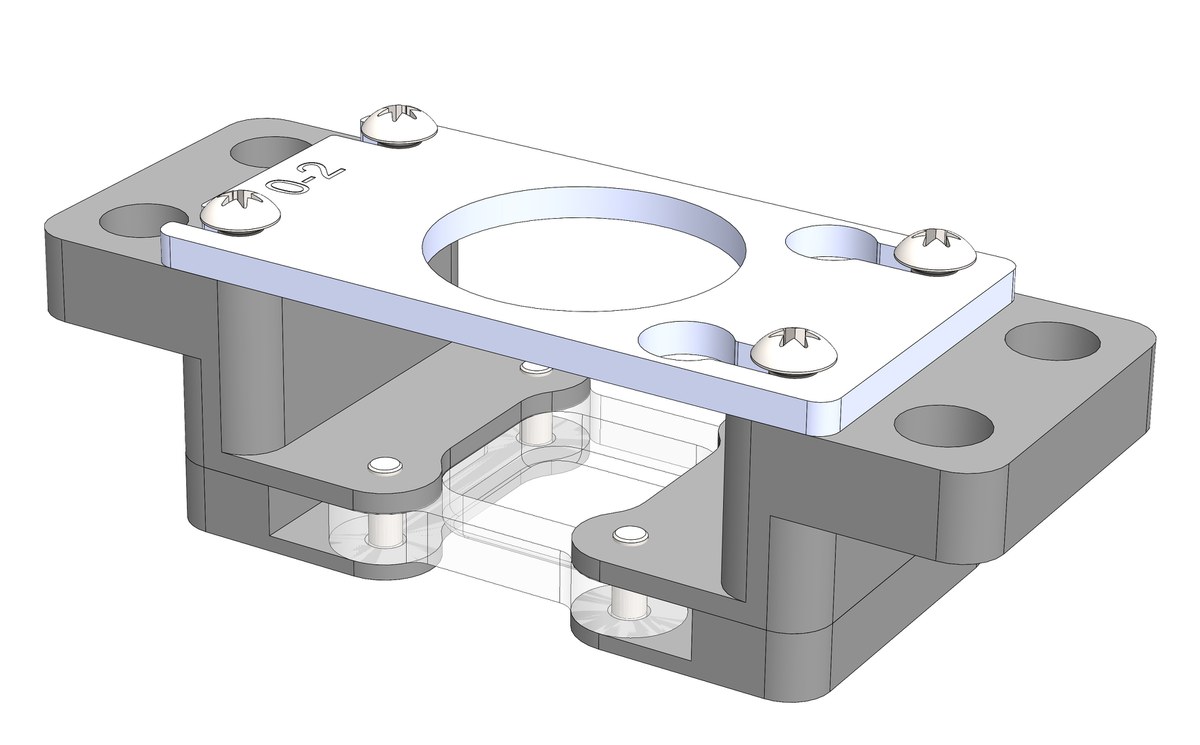
Chamber holder system
The revised cell chamber holder system has been developed in the first to provide for more efficient workflow in the cell stretcher experimentes. The main features are a simple positioning of the silicone chmaber (PDMS) by a clamping mechanism which same force on the silicone chamber. the assembly time as a preparation for the stretch experiment is considerably shortened and facilitated with this system. Not onlyto make time critical cell stretch testa more efficeint, but to help the Staff and reduce the costs incurred. by modifying the design and reducing the component, the microscopy area ist expanded.
contact:
- Institute of Biological Information Processing (IBI)
- Mechanobiology (IBI-2)
Room 1020
