Biomedical image analysis
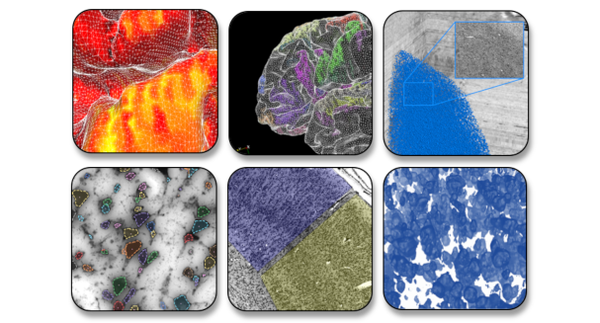
We develop machine learning and computer vision algorithms for processing and analyzing microscopic images in a mostly automated fashion, in order to build maps and extract cellular resolution features from complete series of human whole-brain sections at high throughput. This includes quality control, image enhancement, microstructure detection, image segmentation, and 3D reconstruction for large quantities of 2D microscopic scans.
One of our aims is to shape the next generation of brain mapping. We have shown that it is possible to train Deep Learning networks to segment the human cortex into distinct brain regions and distinguish complex higher associative areas, and are currently populating the BigBrain model with highly detailled 3D cytoarchitectonic maps. Other aspects of our research include detection of neuronal cells, quantification of nerve fiber configurations, and image registration at microscopic precision.
Our team of machine learning experts forms the local research group of Helmholtz AI in Jülich for the research field “Information”. Through this Helmholtz-wide network for applied AI, we aim to share our knowledge and methods across different scientific applications and domains. Due to the high resolution and large quantities of image data that we analyze, we work with researchers at Jülich Supercomputing Centre to run our algorithms efficiently on High Performance Computing (HPC) clusters, and exploit the new generation of modulare supercomputers.
