Surface reconstructions and related local properties of a BiFeO3 thin film
January 2017
by L. Jin, P. X. Xu, Y. Zeng, L. Lu, J. Barthel, T. Schulthess, R. E. Dunin-Borkowski, H. Wang, and C. L. Jia
Coupling between lattice and order parameters, such as polarisation in ferroelectrics and/or polarity in polar structures, has a strong impact on surface relaxation and reconstruction. However, up to now, surface structures that involve the termination of both matrix polarisation and polar atomic planes have received little attention, particularly on the atomic scale.
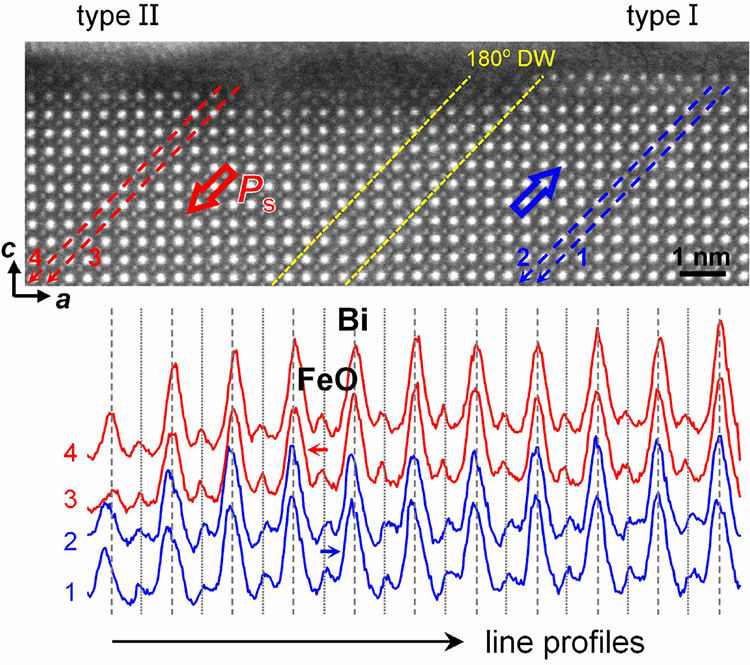
In the present study, surface structures on a BiFeO3 thin film using atomic-resolution scanning transmission electron microscopy and spectroscopy have been studied. Two types of surface structure are found, depending on the polarisation of the underlying ferroelectric domain. On domains that have an upward polarisation component, a layer with an Aurivillius-Bi2O2-like structural unit is observed. Dramatic changes in local properties are measured directly below the surface layer. On domains that have a downward polarisation component, no reconstructions are visible. Calculations based on ab initio density functional theory reproduce the results and are used to interpret the formation of the surface structures.
Further reading:
by L. Jin, P. X. Xu, Y. Zeng, L. Lu, J. Barthel, T. Schulthess, R. E. Dunin-Borkowski, H. Wang, and C. L. Jia:
Surface reconstructions and related local properties of a BiFeO3 thin film,
Scientific Reports 7 (2017) 39698.
