Structural Insights into Ni-stabilized Fe-rich High Voltage Spinels: LiNixFe0.5-xMn1.5O4
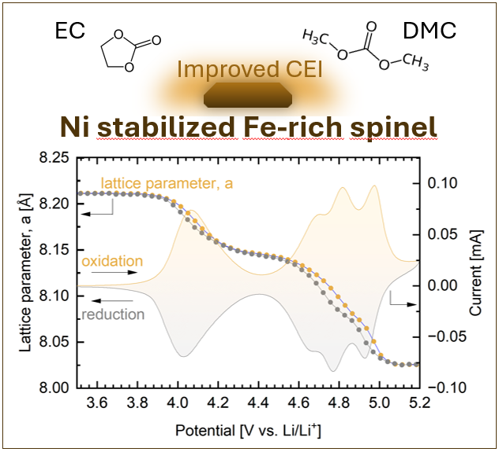
Abstract: Fe-rich high-voltage spinels are attractive positive electrode materials for next-generation Li-ion batteries that offer high resource efficiency and high operating voltages. However, Fe-rich high-voltage spinels do not provide stable cycling performance, especially when compared to the Ni and Co rich members of the high-voltage spinel family. To understand the failure mechanism of Fe-rich high-voltage spinels, we follow the impact of Ni stabilization on the solid solutions LiNixFe0.5-xMn1.5O4 (x = 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5). Electrochemical analysis shows that stable cycling performance can be achieved at relatively low Ni substitution (x = 0.2). Rietveld and pair distribution function analysis show remarkable similarity in average and local structural features, supported by 4D scanning transmission electron microscopy. The cycling mechanism of LiFe0.5Mn1.5O4 and Ni-stabilized LiNi0.2Fe0.3Mn1.5O4 is further compared via in-situ powder X-ray diffraction and in-situ diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy. It is found that the presence of Ni in the electrodes leads to favorable electrolyte-electrode interactions that suppress oxidative reactions and the formation of large concentration polarizations, which is the predominant failure mechanism of LiFe0.5Mn1.5O4.
Cite as: Windmüller, A., Yang, T., Schaps, K., Domgans, A., Zantis, F., Wu, B., Adem, L.H., Olana, B.N., Tsai, C.-L., Yu, S., Raijmakers, L., Kungl, H., Tempel, H., Dunin-Borkowski, R.E., Lin, S.D., Zobel, M., Hwang, B.J. and Eichel, R.-A. (2025), Structural Insights into Ni-Stabilized Fe-Rich High-Voltage Spinels: LiNixFe0.5−xMn1.5O4. Small Struct. 2400691. https://doi.org/10.1002/sstr.202400691
