Perovskite/SHJ tandem solar cells
With single-junction solar cells approaching the Shockley-Queisser limited conversion efficiency, integrating the wide bandgap top perovskite solar cells with crystalline bottom solar cells to form tandem solar cells is considered as a promising strategy for a better utilization of the solar spectrum, in order to further increase solar cell efficiency. In IMD-3, we aim at bringing our advantages in high efficiency silicon heterojunction (SHJ) solar cell and perovskite solar cell development together, to develop a perovskite/SHJ tandem technology with efficiency above 30%.
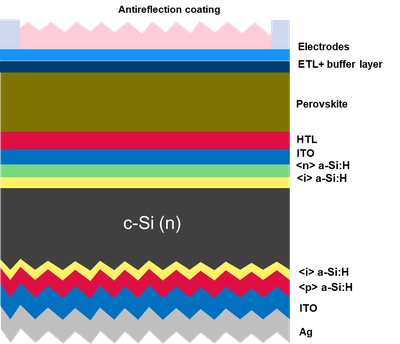
Research Topics:
- Optimization of the SHJ bottom cell
- High efficiency SHJ solar cells based on different wafer strategy, such as single-side textured wafer, two-side nano-sized textured wafer
- Soft deposition of transparent conductive layer
- Optimization of perovskite top cell
- Soft deposition of transparent electrodes
- Exploration of suitable hole transport layers (metal oxides, polymers, small molecules and self-assembled monolayers)
- Bandgap tuning by varying perovskite composition
- Electron transport layer process development via Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) and/or spin coating techniques
- Optimization of tandem device
- Process development of perovskite deposition on different SHJ bottom cells
- Current matching between top and bottom cells
- Optimization of intermediate recombination layer
- Optimization of opto-electrical design for tandem by advanced device simulation
- Design of front and interlayers with micro-/nano-optical approaches
- Reduction of power losses at the interlayers by improved engineering of the layer stack
Dr. Kaining Ding
Head of Silicon Heterojunction Solar Cells and Modules Department
- Institute of Energy Materials and Devices (IMD)
- Photovoltaics (IMD-3)
Building 02.6 /
Room 4004
Room 4004
+49 2461/61-1604
E-Mail
Last Modified: 11.07.2024

