Cognitive and Neurometabolic Effects of Creatine
Creatine improves cognitive performance during sleep deprivation
Creatine is a popular dietary supplement in the sports community. It is found in foods and can also be produced by the body. According to studies, creatine has the potential to counteract the cognitive impairment caused by sleep deprivation. In a randomized longitudinal study, effects of a high dose of creatine (0.35 g/kg) on neurometabolic processes and cognitive performance during sleep deprivation was investigated.


From the third hour after creatine administration onwards, a positive effect on brain metabolism and cognitive performance was observed which lasted up to nine hours. In particular, processing time and short-term memory improved.

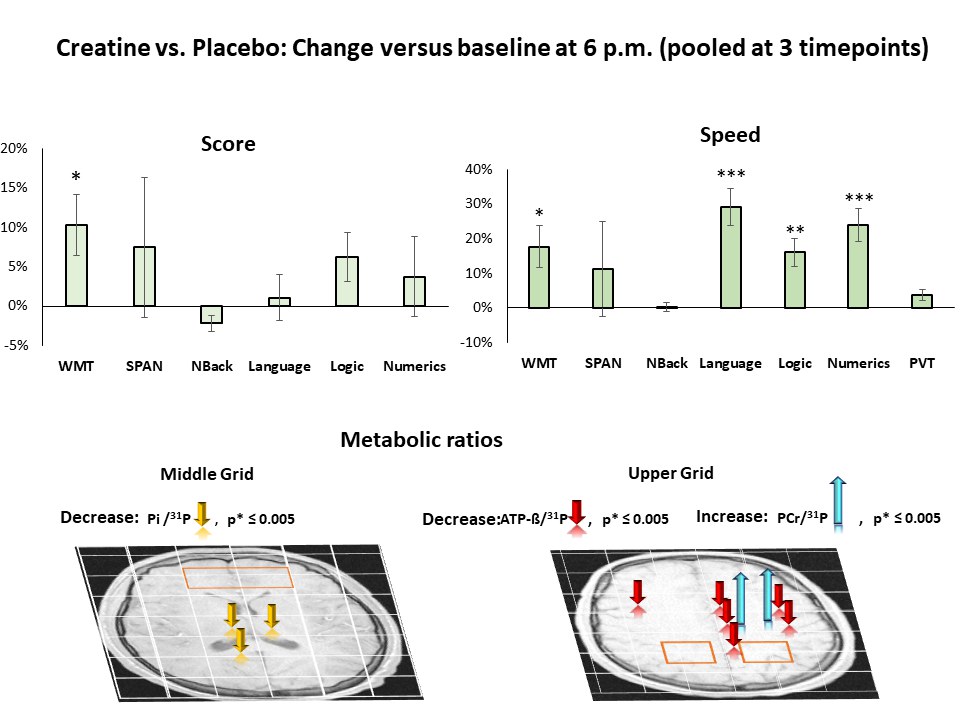
These results suggest that a single, high dose of creatine improves cognitive performance and causes changes in the brain's energy reserves during sleep deprivation. However, for the time being, taking such a high dose in private settings is not recommended, as high doses of creatine can put a strain on the kidneys and cause health risks.
