fMRI
FUNCTIONAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING
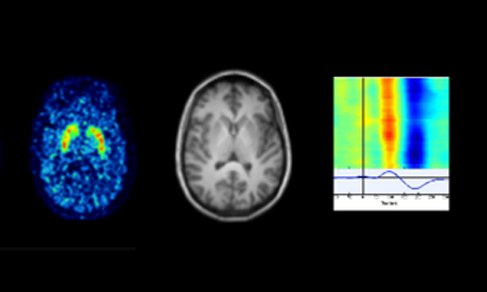
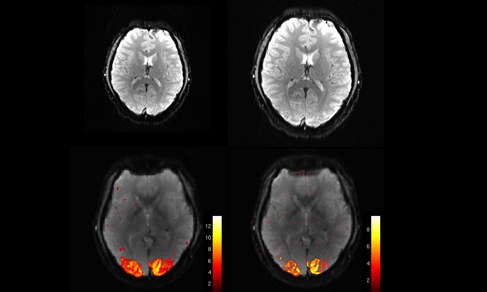
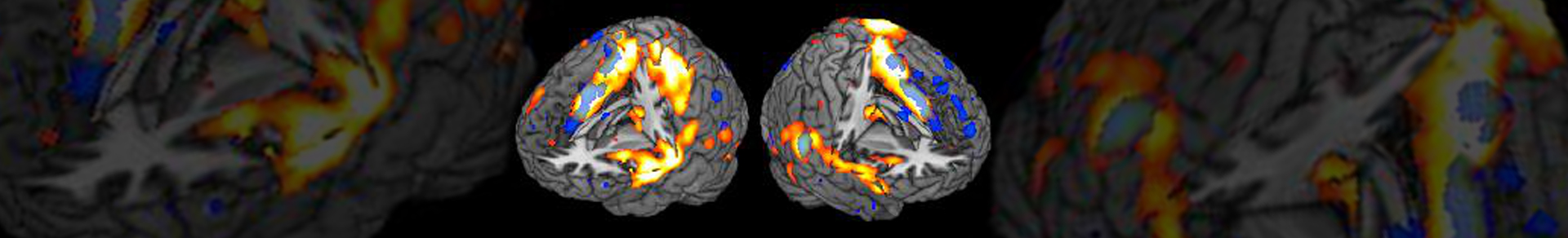
In functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), the so-called blood oxygenation level dependent (BOLD) contrast is utilized to map brain activation in healthy subjects or in neurological or psychiatric patients. In a non-invasive way, fMRI enables researchers to map brain activation e.g., during the brain's resting state, cognitive processing, emotional or somatosensory experiences.
In addition to the characterization of activation patterns of distinct neurocognitive processes, such as inhibitory performance, working memory and processing of speech, this fMRI group focuses on the implementation new fMRI techniques into the scanner environment. Specifically, the group's main focus is to enrich fMRI data with results from other brain imaging techniques, e.g., EEG, PET and MEG to allow for a more detailed characterization of cerebral activation.
Moreover, the group trains study participants to learn to voluntarily modulate their own brain activation applying real-time fMRI and neurofeedback.
Several studies of the fMRI group are carried out in close collaboration with national and international external groups, for instance at the RWTH Aachen University, the University of Maastricht and the University of California San Diego.
Project leader
- Institute of Neurosciences and Medicine (INM)
- Medical Imaging Physics (INM-4)
Room 211
Staff
Dr. Seong Dae Yun
Senior scientist, Team leader of Sequence & Scientific Computing
- Institute of Neurosciences and Medicine (INM)
- Medical Imaging Physics (INM-4)
Room R 231