MAGIC
The instrument MAGIC [1-3] is a neutron diffractometer under construction at the European Spallation Source (ESS) in a collaborative contribution of the in-kind partners Laboratoire Léon Brillouin (France), Paul-Scherrer Institute (Switzerland) and Forschungszentrum Jülich (Germany). The project will be completed in 2027 with the end of cold commissioning.
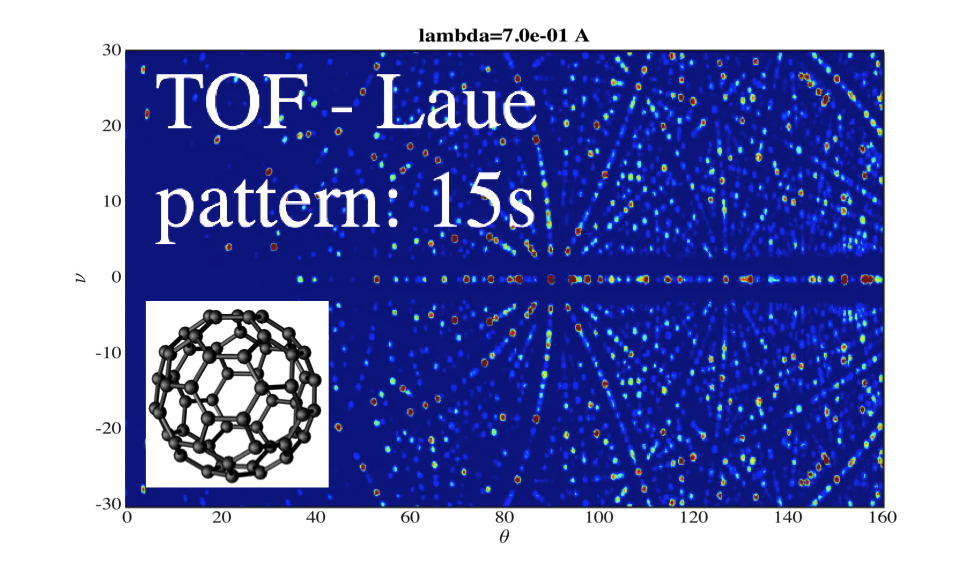
MAGIC is a single crystal diffractometer uniquely combined with neutron polarisation dedicated to the broad research field of magnetism with applications from magnetic structure refinement to magnetic diffuse scattering. The combination of the TOF-Laue technique with a large detector and the intense long pulse of ESS yields a new efficiency allowing for even "x-ray sized" crystals and epitaxial films studies. The permanent use of polarisation and availability of extreme sample environment (temperature, field and pressure) ensures the instrument will be of great benefit to the large magnetism community.
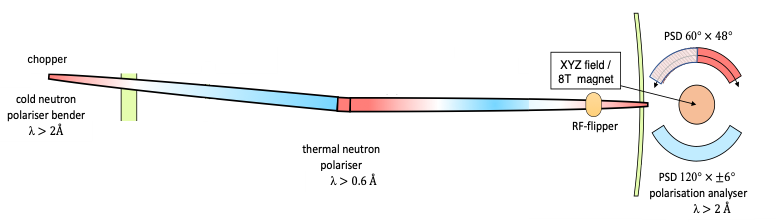
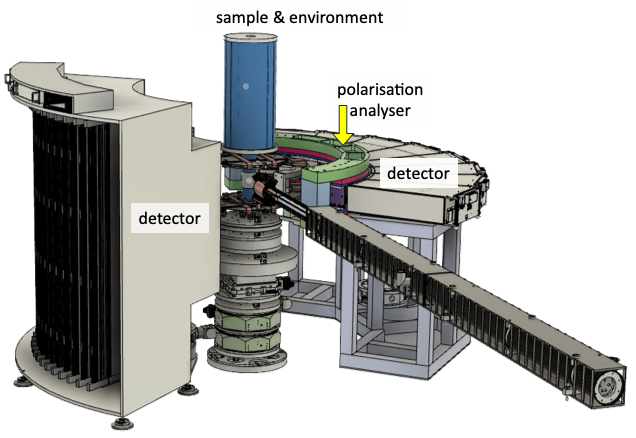
The layout of the MAGIC instrument. Standard options use either thermal polarised neutrons and a 8T magnet, or cold neutrons and polarisation analysis with XYZ fields. The set-up for the latter option is shown to the right.
To cover the needs for both Bragg diffraction and diffuse scattering, MAGiC will make full use of the optimized peak fluxes of the thermal and cold ESS moderators. The possibility to choose between thermal or cold fluxes will ensure MAGiC high versatility, by using cold neutrons with polarisation analysis for high Q-resolution studies of complex magnetic structures as well as for magnetic diffuse scattering, and thermal neutrons to cover a high Q-space studying magnetic properties under high magnetic fields. Utilizing most recent developments in neutron optics, MAGiC will have a highly-polarized beam (P > 98%) from 0.6 to 6Å with a flux in the order of 10⁹ n/s/cm² at the sample position. A new detector technology based on multiple solid B-10 converters in inclined geometry will combine high efficiency (60% at 1Å) and high spatial resolution (1mm) with a count rate capability exceeding those of current He-3 detectors by more than an order of magnitude.
MAGIC Team
European Spallation Source: Denis Vasiukov (starting Dec 2024)
Forschungszentrum Jülich: Werner Schweika, Peter Harbott
Laboratoire Léon Brillouin: Xavier Fabreges, Sergey Klimko, Arsen Gukasov
Paul-Scherrer Institute: Christine Klauser, Artur Glavic
References & Links
[1] MAGIC instrument description
[2] W. Schweika, H. Soltner, C. Klauser, S. Klimko, A. Gukasov, X. Fabrèges, Polarised neutrons and polarisation analysis at the ESS instrument MAGIC, IUCR 2023 Melbourne, Acta Cryst. (2023). A79, C472, https://doi.org/10.1107/S205327332309143X
[3] K.H. Anderson et al. The instrument suite of the European Spallation Source, (2020), Nuclear Inst. and Methods in Physics Research A957, 163402.
