Multiparticle Collision Dynamics-based schemes
Using Multiparticle collision (MPC) dynamics, a particle-based hydrodynamic simulation approach which captures hydrodynamic interactions and thermal fluctuations, we develop in collaboration with IBI-4 and IBI-5 institutes a two-fluids MPC scheme mimicking a membrane environment embedded in a solvent. The proposed MPC fluid-layer model can be straightforwardly implemented, and it is computationally very efficient. The aim is to create a computational platform for mesoscopic simulations of the diffusion and phase behavior of assemblies of interacting proteins attached to or embedded inside a membrane.
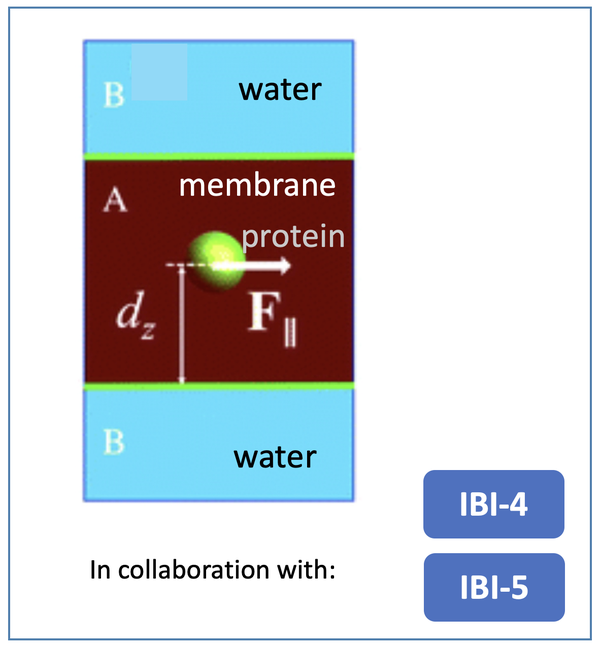
Within the two-fluids MPC scheme, two layered immiscible fluids A and B of different shear viscosities are separated by planar interfaces, mimicking a membrane environment embedded in a solvent. The measured hydrodynamic mobilities of an embedded colloidal sphere are in good agreement with hydrodynamic force multipoles calculations, for a no-slip sphere moving under creeping flow conditions near a clean, ideally flat interface [1].
People involved
Dr. Vania Calandrini
Group leader
Collaborators
Prof. Dr. Gerhard Naegele
Senior scientist
- Institute of Biological Information Processing (IBI)
- Biomacromolecular Systems and Processes (IBI-4)
Room 106
Prof. Jan K.G. Dhont
Senior scientist
- Institute of Biological Information Processing (IBI)
- Biomacromolecular Systems and Processes (IBI-4)
Room 77
References
- Z. Tan, V. Calandrini, J.K. Dhont, G. Naegele, R. Winkler, Hydrodynamics of immiscible binary fluids with viscosity contrast: a multiparticle collision dynamics approach, Soft Matter, 2021,17, 7978-7990.



