Enhanced AI Model Boosts Global Geospatial Analytic Capabilities
In collaboration with NASA and IBM Research JSC released an expanded version of the open-source geospatial artificial intelligence (AI) foundation model, Prithvi-EO. The updated model (Prithvi-EO-2.0) supports a broader range of geographical applications: It integrates global satellite data, enabling advanced Earth observation applications such as tracking land use changes, disaster monitoring, crop yield prediction, and environmental analysis on a planetary scale.

Prithvi-EO-2.0 was pre-trained on the JSC’s JUWELS Booster Module using 240 NVIDIA A100 GPUs. It is now available on Hugging Face with new 300M and 600M parameter models that incorporate temporal and location embeddings. A technical paper is available on arXiv.
JSC’s SDL (Simulation and Data Lab) AI and ML for Remote Sensing aims to increase the adoption of interdisciplinary research combining remote sensing applications, AI, and high-performance and innovative computing. Being an integral part of the work on Prithvi-EO-2.0 is an important step towards that aim. The SDL is strongly connected with the University of Iceland and the IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Society (GRSS), which were instrumental for the collaboration with NASA and IBM Research.
“Looking ahead, JUPITER’s operational phase is set to push Prithvi-EO even further by leveraging exascale computing resources, providing the Earth observation community with even more powerful tools for their applications,” says Dr. Rocco Sedona, deputy head of the SDL AI and ML for Remote Sensing . “Prithvi-EO-2.0 represents a significant step forward in global geospatial analysis, offering robust, open-source solutions to address pressing environmental challenges,” Prof. Gabriele Cavallaro, head of the lab, adds. “We are very happy to contribute to this significant development.”
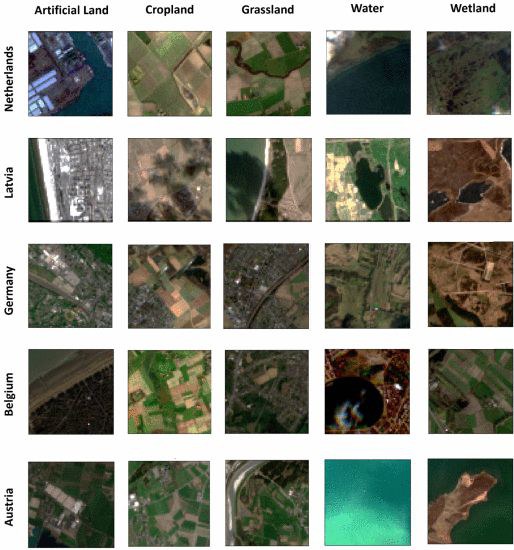
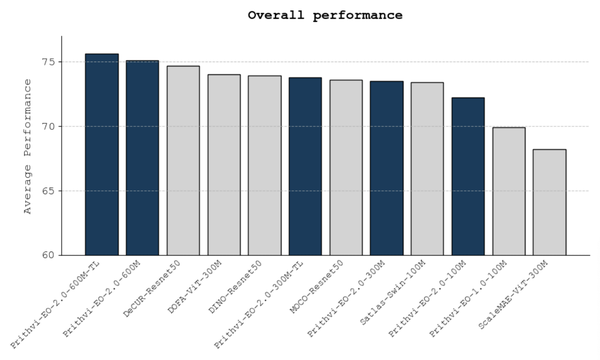
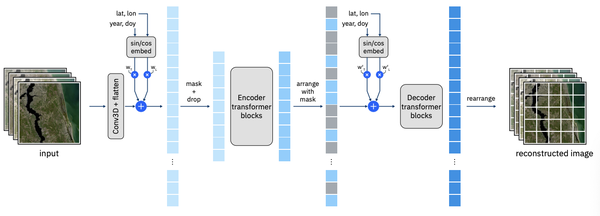
Originally launched in August 2023, Prithvi-EO was pre-trained on NASA's Harmonized Landsat and Sentinel-2 (HLS) dataset and leveraged the Vision Transformer (ViT) architecture using a masked autoencoder (MAE) approach. Prithvi-EO-2.0, its new version, achieves improved performance across various geospatial tasks. It has been trained on 4.2 million global time series samples from HLS covering diverse ecoregions and landscapes worldwide.
For more information about research and work activities of the SDL “AI and ML for Remote Sensing, visit https://www.fz-juelich.de/en/ias/jsc/about-us/structure/simulation-and-data-labs/sdl-ai-ml-remote-sensing
Official NASA Press Release: Expanded AI Model with Global Data Enhances Earth Science Applications - NASA Science
Contact: Rocco Sedona (JSC), Gabriele Cavallaro (JSC, University of Iceland)
