ApoTome Fluorescence Microscope

Model:
- ZEISS Axio Imager Z1
Features:
- Microscope: Axio Imager Z1 with 6 objectives: 10x Water, 20x Water, 63x Water, 40x Oil, 63x Oil and 20x Air.
- UV light source Illuminator HXP120. HAL100 halogen light source for DIC and PC imaging.
- Filter sets: 49 (DAPI), 38HE (GFP), 43HE (DsRed), 50 (Cy5), 46HE (YFP), 47 (CFP), 62HE (BFP/GFP) and Analy DIC TransLight, plus other options.
- Digital CCD camera: AxioCam MR R3 (black/white)
- Imaging software: ZEN blue edition 2012
- ApoTome slider and control box
Applications:

ApoTome is an innovative slider module providing structured illumination for fluorescence microscopy. The microscope can produce high quality 2D and 3D digital images for fixed or living cells or tissues:
1. Mutiple images or multi-channel images (transmitted light and/or fluorescence) in the format of 2D or Z-stack:
To enable the automatic generation of Z-stack images, the software controls the z-drive of a motorized microscope in precise steps, synchronizing it with the image acquisition. You can either determine the focusing interval yourself or have it automatically computed for highest sample accuracy. The advantage of this module is the optimal detection of information in the third dimension.
2. Tiles function for single or multi-channel images:

Developed for analyzing large surfaces, Tiles scans the area of your specimens in just one process. A virtual overall image is then generated from individual tiles, which serves perfectly as an overview image for navigation around the sample or as a basis for further analyses. Measurements can be performed on the Tiles image across the boundaries of the different frames – the tiles do not pose any restriction.
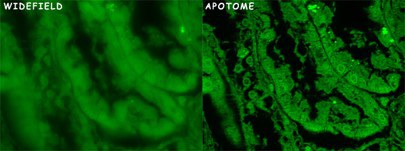
3. Optical sectioning using structured illumination (ApoTome)
In thick specimens, the signal from the focal plane is compromised by the out of focus light coming from planes above and bellows this plane. The result is a blurred, low contrast image. In this condition, is not possible to render a three-dimensional projection of the specimen.
Some techniques were developed to remove the out of focus light, either optically (Confocal) or mathematically (Apotome).
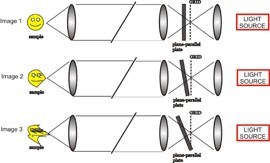
In the ApoTome, a grid is inserted in the illumination pathway of a conventional fluorescence microscope. A plane-parallel glass plate is placed in front of the grid and it tilts back and forth projecting the grid in the image in 3 different positions. For each depth, 3 raw images with the projected grid superimposed in 3 different positions are taken. The software uses the projected images of the grid to calculate and removes the out of focus light. The principle is, if the grid is visible that information is in focus. If not, that signal corresponds to out of focus light and it is removed from the final image. The software combines the 3 images into 1 for each stack.
More information:
http://www.zeiss.com/microscopy/en_de/products/imaging-systems/apotome-2-for-biology.html
http://www.robarts.ca/confocal/techniques.html
Contact:
Prof. Dr. Andreas Offenhäusser
Tel.: +49-2461-61-2330
e-mail: a.offenhaeusser@fz-juelich.de
