PlasmaPhysics-PlasmaSurfaceInteraction.poster.png
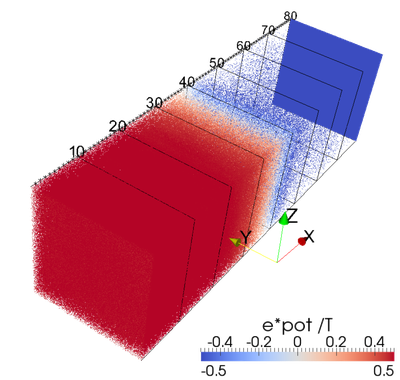
Development of a plasma sheath at a conducting wall (blue) with freely floating potential. Thermal plasma ions and electrons are injected from the opposite boundary, where they travel freely up to the wall and are either absorbed or reflected. After a transitional period (displayed here), a quasi-stationary equilibrium is reached yielding quantifiable particle fluxes and damage rates at the wall.
Last Modified: 24.01.2022
