Interactions, Phase Behaviour and Dynamics
The “softness” of a colloidal particle results from two contributions i) the deformability of the individual particle, its “intramolecular softness”, and ii) the form and range of particle interactions in terms of an effective potential, its “intermolecular softness”.
Soft, long-range repulsive interactions are ubiquitous in soft matter materials. Typically, these are generated either by steric/entropic repulsion, i.e. by a polymeric layer grafted on the particle surface, or by electrostatic/enthalpic repulsion by generating ionic sites on the particle surface. This leads to the well-known classes of sterically stabilized or charge stabilized colloids.
In recent projects, we established neutral amphiphilic block copolymer micelles as a model system for sterically stabilized colloids and investigated phase behaviour and dynamics finding convincing agreement between experiment and theory without any adjustable parameter.
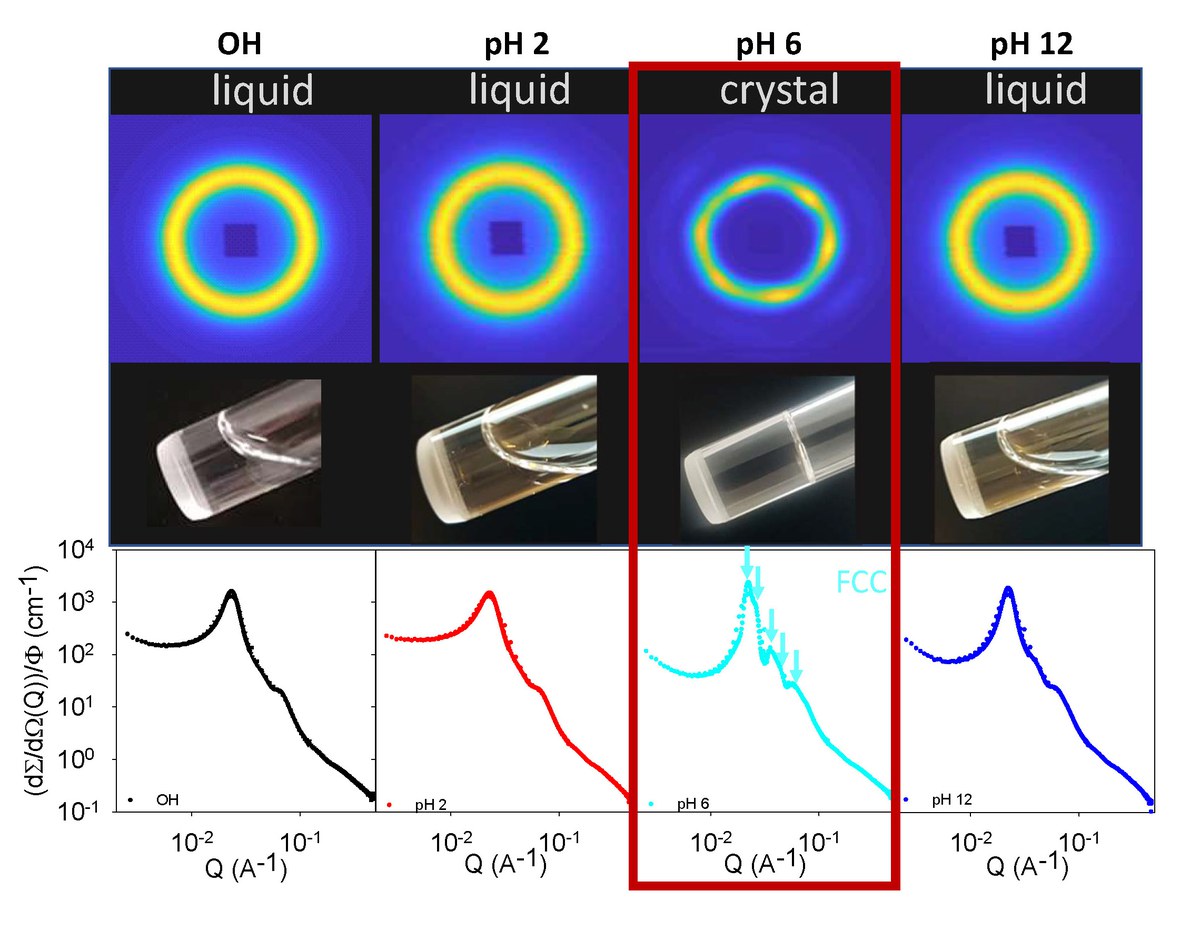
In current projects, we investigate particles combining properties of sterically and electrostatically stabilized colloids. Due to selective end-group oxidation, all charge carriers are only on the particle surface. Their number can be precisely adjusted by pH value and stoichiometry, so it is possible to "switch" between steric or electrostatic stabilization. By means of neutron scattering, structure and interactions could be elucidated in detail and quantitatively understood by comparison with modern theories on microscopic scales. The type and strength of stabilization has a major influence on macroscopic flow and phase behaviour, as additional rheological studies show.
Such duplex soft colloids can be considered as hybrid materials connecting properties of neutral and polyelectrolyte block copolymer micelles as well as those of non-ionic and ionic surfactants. The properties of such duplex soft colloids may bridge the gap to biological materials where both kinds of soft interactions determine the function and solubility of proteins, for example.
References:
S. Gupta, M. Camargo, J. Stellbrink, J. Allgaier, A. Radulescu, P. Lindner, E. Zaccarelli, C. N. Likos and D. Richter
Phase diagram of soft nanocolloids
Nanoscale 7 13924, 2015
L. Tea, L. Willner, C. Waldorf, O. Matsarskaia, R. Schweins, S. Förster, L. Willner, and J. Stellbrink
Surface Charged Polymeric Micelles - A Tunable Model System Studied by SANS
Macromolecules 57 5818, 2024
Contact:
- Jülich Centre for Neutron Science (JCNS)
- Neutron Scattering and Soft Matter (JCNS-1)
Room R 273

