Benefits and limits of biological nitrification inhibitors for plant nitrogen uptake and the environment
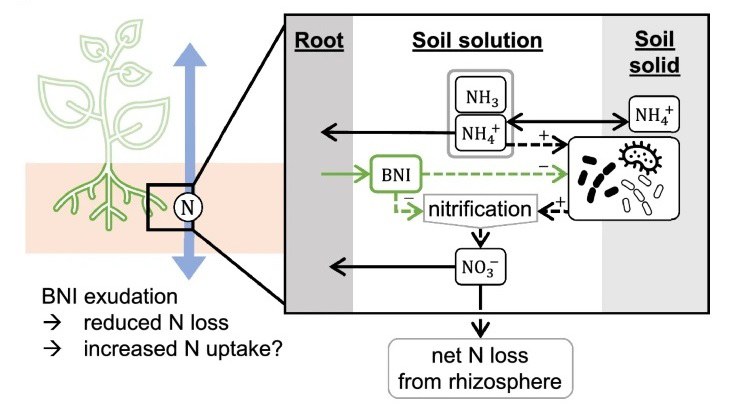
Nitrate is a pollutant but also a macro-nutrient for plants, and product of nitrification by soil microorganisms. Plants can inhibit nitrification, which reduces N loss to the environment, but not necessarily increases plant N uptake, and a model showed under what conditions.
Read the paper:
Published in Microbiology, Protocols & Methods, and Plant Science
Jul 17, 2024
Abstract
Plant growth and high yields are secured by intensive use of nitrogen (N) fertilizer, which, however, pollutes the environment, especially when N is in the form of nitrate. Ammonium is oxidized to nitrate by nitrifiers, but roots can release biological nitrification inhibitors (BNIs). Under what conditions does root-exudation of BNIs facilitate nitrogen N uptake and reduce pollution by N loss to the environment? We modeled the spatial–temporal dynamics of nitrifiers, ammonium, nitrate, and BNIs around a root and simulated root N uptake and net rhizosphere N loss over the plant’s life cycle. We determined the sensitivity of N uptake and loss to variations in the parameter values, testing a broad range of soil–plant-microbial conditions, including concentrations, diffusion, sorption, nitrification, population growth, and uptake kinetics. An increase in BNI exudation reduces net N loss and, under most conditions, increases plant N uptake. BNIs decrease uptake in the case of (1) low ammonium concentrations, (2) high ammonium adsorption to the soil, (3) rapid nitrate- or slow ammonium uptake by the plant, and (4) a slowly growing or (5) fast-declining nitrifier population. Bactericidal inhibitors facilitate uptake more than bacteriostatic ones. Some nitrification, however, is necessary to maximize uptake by both ammonium and nitrate transporter systems. An increase in BNI exudation should be co-selected with improved ammonium uptake. BNIs can reduce N uptake, which may explain why not all species exude BNIs but have a generally positive effect on the environment by increasing rhizosphere N retention.
Contact
Dr. Johannes Auke Postma
Head of research- Root Dynamics group
- Institut für Bio- und Geowissenschaften (IBG)
- Pflanzenwissenschaften (IBG-2)
Raum 015
- Institut für Bio- und Geowissenschaften (IBG)
- Pflanzenwissenschaften (IBG-2)
Raum 013