Joining forces to efficiently improve biocatalysts for sustainable biotechnology
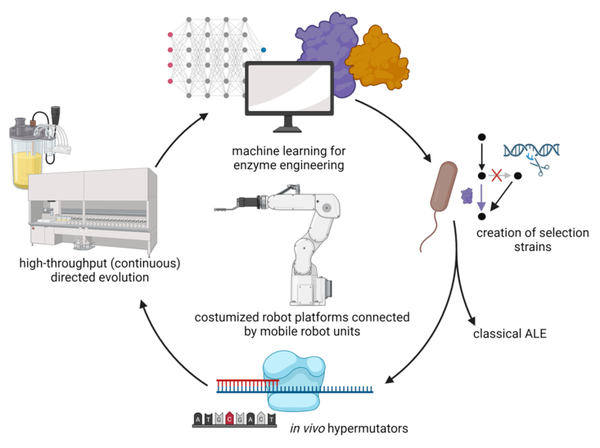
The replacement of current industrial production methods for chemicals with more sustainable biotechnological processes is urgently required to reduce the consumption of fossil raw materials and the production of greenhouse gases. The development of cost-effective bio-based processes requires the creation of stable and selective enzymes that serve as efficient biocatalysts. However, the modification and testing of improved enzymes using traditional methods is a slow and labor-intensive method. To speed up the process of enzyme engineering, new strategies like directed evolution are becoming more popular. Furthermore, computational tools, especially machine learning, help to expand the possibilities for enzyme engineering.
Now, an international team including scientists from the Charité in Berlin (Germany), the Technical University of Denmark, Leiden University (the Netherlands), and the IBG-1 from Forschungszentrum Jülich (Germany) propose to combine machine learning with automated workflows and efficient selection processes in genetically engineered bacteria to address challenges in enzyme engineering.
This new Perspective was published in Nature Communications:
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-46574-4