Novel Solvent-Based Electrolytes for Enhanced Lithium-Ion Battery Performance
TO-179 • PT 1.3114 • As of 07/2024
Institute of Energy Materials and Devices
Ionics in Energy Storage (IMD-4 / HI MS)
Technology
We introduce a novel class of solvent-based electrolytes designed for electrochemical energy storage systems, particularly lithium-ion batteries, utilizing cyclic acetals as solvents. These electrolytes consist of at least one solvent and one conductive salt, which can include well-known lithium salts such as LiTFSI (LiC2NO4F6S2) or LiPF6. The use of cyclic acetals, derived from renewable resources like modified sugar alcohols, enhances the sustainability of the electrolytes. These solvents not only provide high ionic conductivity but also improve the contact between the electrolyte and electrodes compared to solid-state electrolytes. Additionally, the chemical structure of these cyclic acetals ensures high chemical stability and a broad electrochemical stability window, making them suitable for a wide range of applications in energy storage technologies.
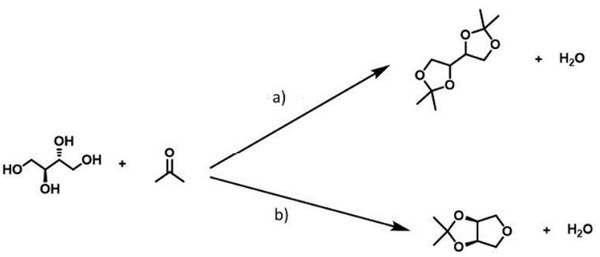
Problem addressed
Conventional electrolytes, whether solvent-based or solid, often struggle with stability and ionic properties, which are crucial for high-voltage applications. For instance, aqueous electrolytes, especially concentrated water-in-salt types, require high concentrations of conductive salts to achieve adequate electrochemical stability. This reliance on high salt concentrations can lead to inefficiencies and increased costs. On the other hand, non-aqueous organic electrolytes, while commonly used, also present issues related to their structural complexity and potential environmental impacts. Overall, conventional technologies exhibit limitations in ionic conductivity and electrochemical stability, particularly when aiming to minimize the use of conductive salts. Our novel approach aims to address these shortcomings by providing an improved electrolyte that requires less conductive salt, thereby enhancing performance and sustainability in future energy storage solutions.
Solution
Our innovative solvent-based electrolytes offer several significant advantages over traditional electrolyte solutions. Firstly, they exhibit higher conductivity and better performance in terms of ion transport, particularly for lithium ions, which is crucial for efficient battery operation. The incorporation of cyclic acetals also allows for a reduction in the amount of conductive salt required for aqueous electrolytes, leading to cost savings and resource conservation. Furthermore, these electrolytes can be formulated to be less flammable, enhancing safety during use. The potential for using water as a co-solvent not only improves safety but also contributes to the overall sustainability of the product. By minimizing the reliance on hazardous materials and utilising renewable resources, this technology aligns with the growing demand for environmentally friendly energy storage solutions.
Benefits and Potential Use
The described solvent-based electrolytes are versatile and can be applied in various electrochemical energy storage systems, including lithium-ion, sodium, and zinc-ion batteries. Their high ionic conductivity and stability make them ideal for use in commercial battery cells, where they can significantly enhance performance and safety. The ability to tailor the electrolyte properties through the selection of solvents and additives allows for customization to meet specific application requirements. Additionally, the straightforward synthesis process of these electrolytes facilitates scalability, making them suitable for large-scale production. As the demand for efficient and sustainable energy storage solutions continues to rise, potential licensees can leverage this innovative technology to gain a competitive edge in the market.
Development Status and Next Steps
Our technology is continuously being enhanced. Our Institute of Energy Materials and Devices – Ionics in Energy Storage (IMD-4 / HI MS) already cooperates with numerous national and international companies and scientific partners. Forschungszentrum Jülich focuses on energy and cost-efficient devices suitable for application in various emerging technologies. We are thus constantly seeking cooperation partners and/or licensees in this field and adjacent areas of research and applications.
TRL
3
Keywords
Solvent-based Electrolytes, Lithium-ion Batteries, Cyclic Acetals, Conductive Salts, Ionic Conductivity, Water-in-Salt Electrolytes, Sustainable Solvents
